Jobs in the Energy Sector: How Solar and Hydrogen Power are Shaping the Future
The renewable energy sector has cemented its place as a key driver of employment growth, offering both economic and environmental…
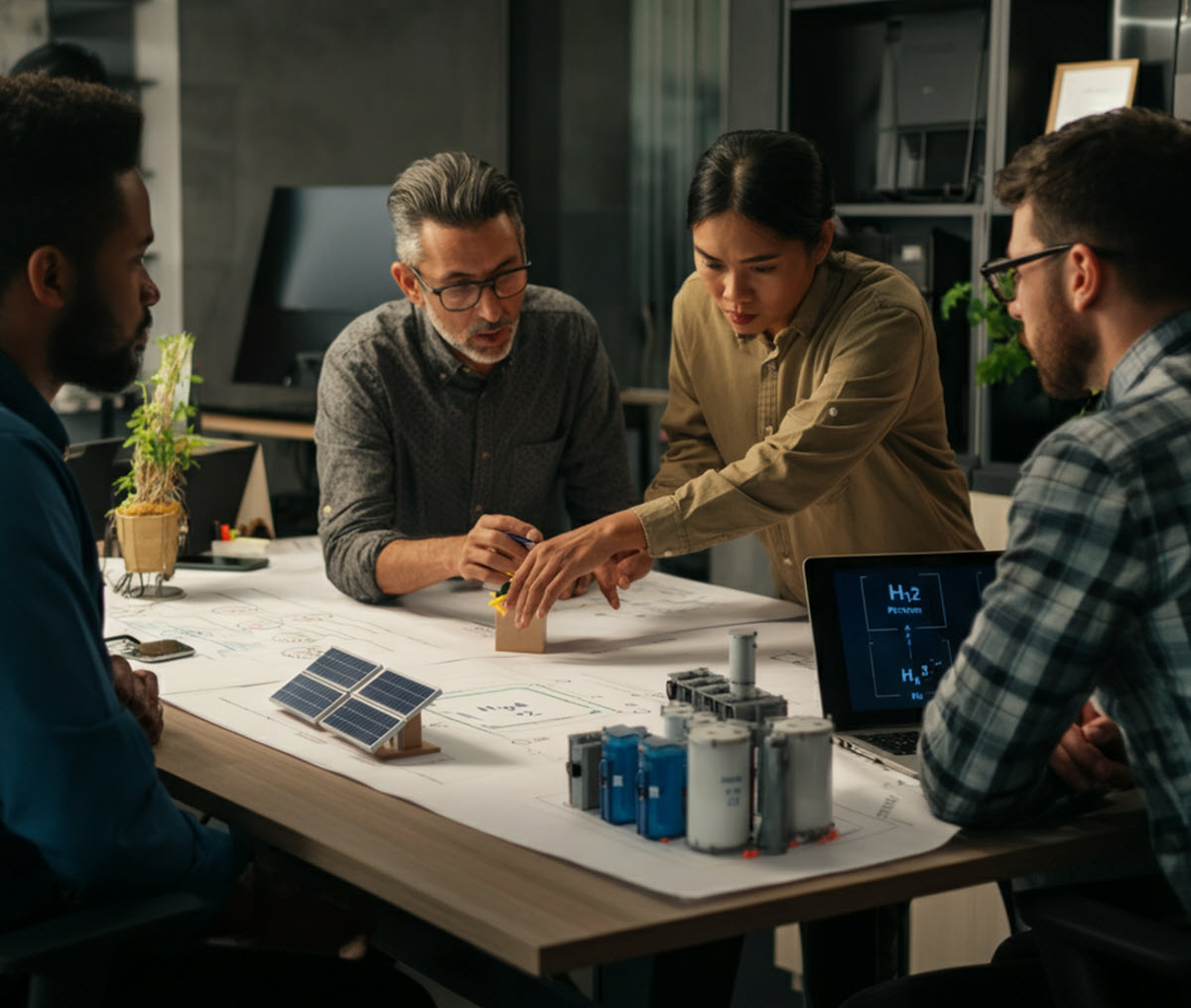

The renewable energy sector has cemented its place as a key driver of employment growth, offering both economic and environmental advantages. With solar energy already making a substantial impact on global job markets and hydrogen power poised to emerge as the next big player, these renewable energy sources are transforming the employment landscape. Here, we explore the job boom driven by solar energy, the promising potential of hydrogen technologies, and the critical roles fueling this green transition.
The Solar Energy Job Boom
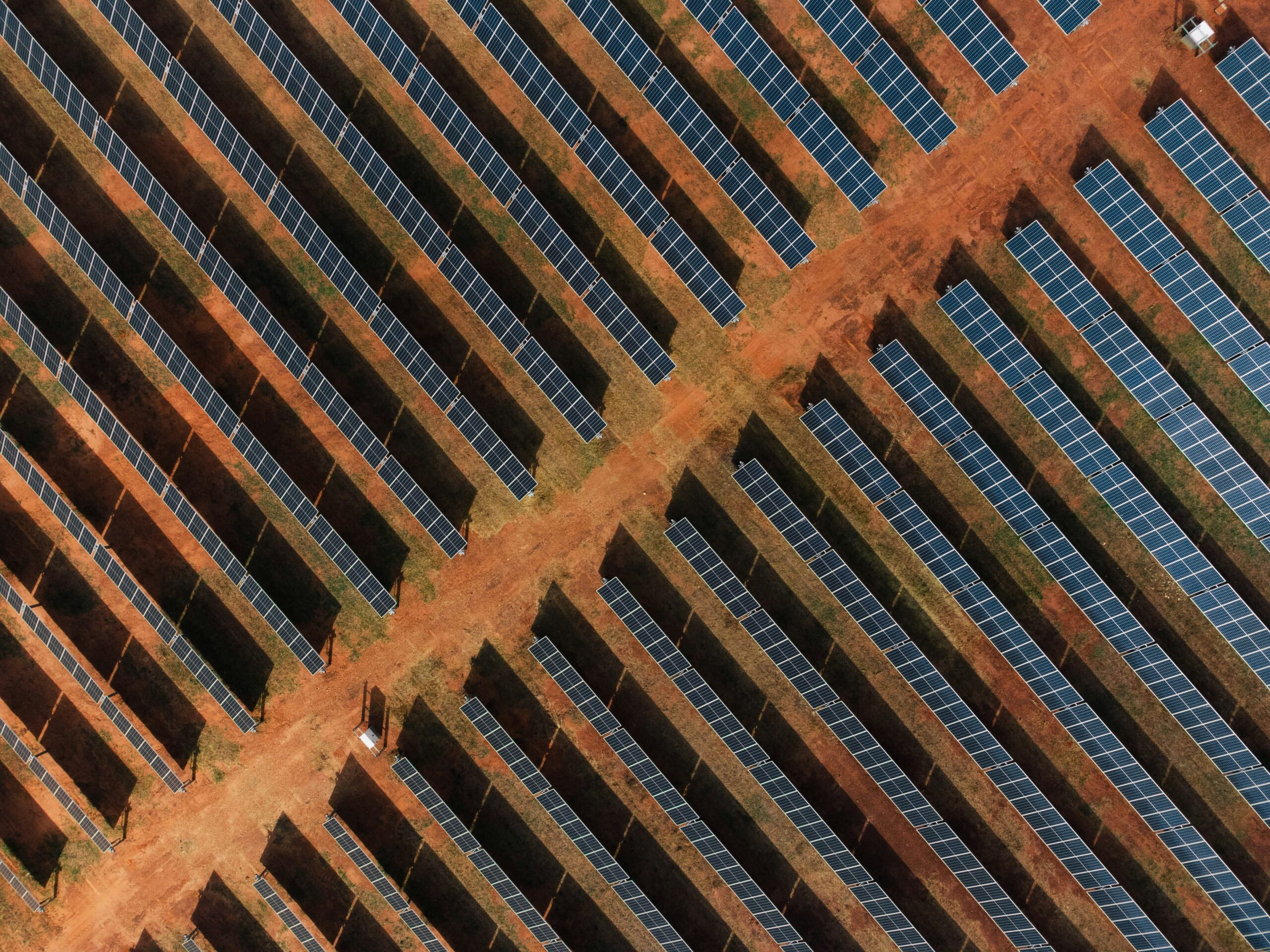
The solar power sector has been a powerhouse for jobs in energy, surpassing many traditional energy industries. According to the National Solar Jobs Census, the U.S. solar industry employed 279,447 workers by the end of 2023, representing a 5.9% rise compared to 2022. This growth continues a steady trend, with solar jobs increasing by 14% over the past five years, while installed capacity surged by an astounding 271%.
Massive investments in residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar projects have generated employment opportunities across a spectrum of roles. Installation and project development alone accounted for nearly 64% of solar jobs in 2023, with roles ranging from technicians to construction planners. Meanwhile, manufacturing and operations and maintenance roles are also on the rise, reflecting the industry’s need for skilled workers to sustain existing systems while developing advanced technologies.
Globally, solar energy employed about 3.4 million people in 2020, and that number is anticipated to climb further. Countries like India and the United States are investing heavily in solar infrastructure, fostering employment in manufacturing, installation, sales, and beyond. Beyond job creation, the economic ripple effect of solar energy is evident in reduced energy costs, elevated property values, and bolstered small businesses. The industry’s stability and scalability make it a long-term investment for both workers and investors.
Hydrogen Power: The Next Frontier
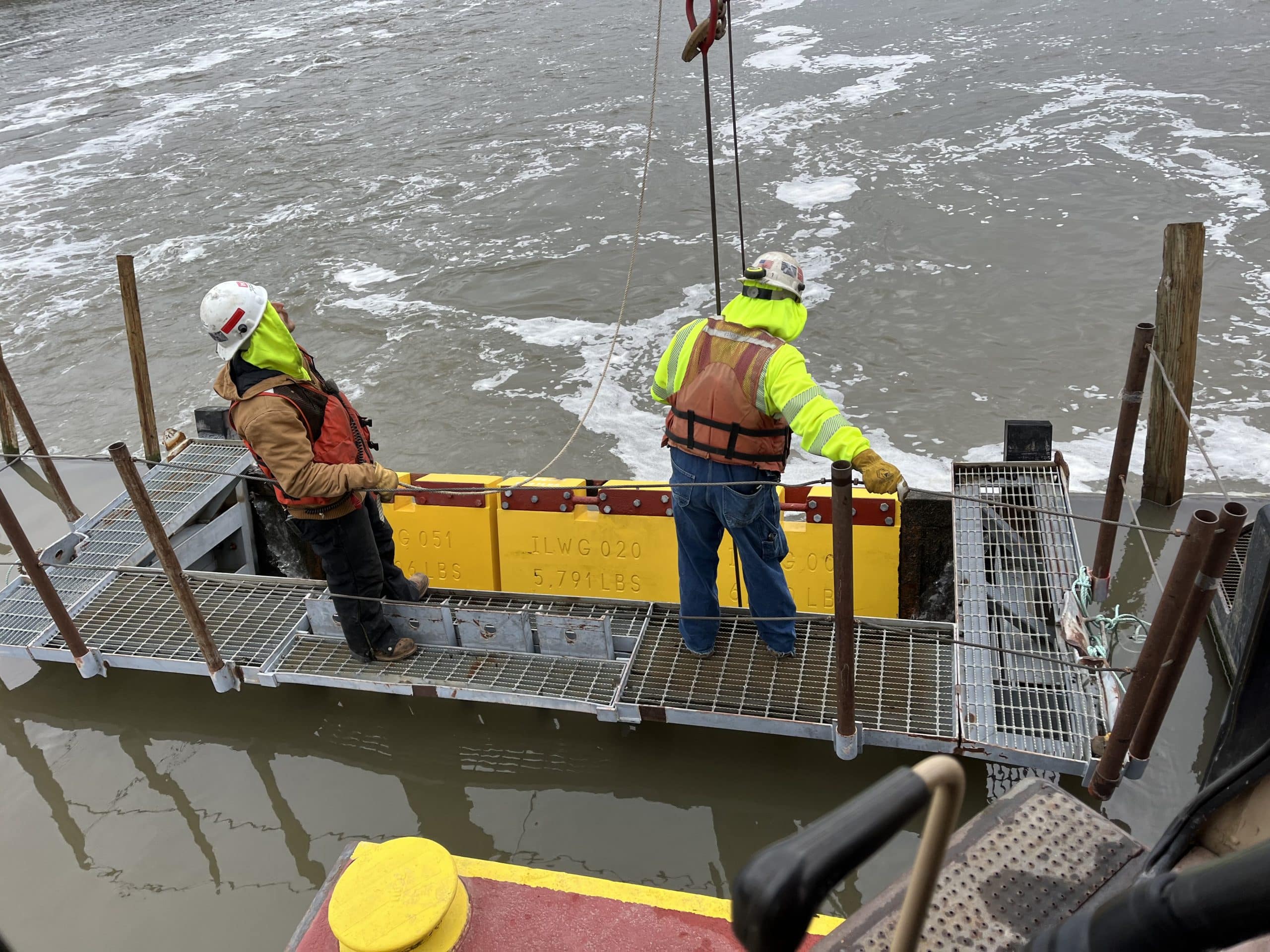
While solar energy has already demonstrated its potential, hydrogen power is emerging as an exciting prospect for future energy employment. Often referred to as the “Swiss army knife” of clean energy, hydrogen can be produced anywhere using renewable resources, fossil fuels with carbon capture, or even nuclear energy, giving it unmatched versatility.
The growing global interest in hydrogen technologies signals tremendous potential for job creation. Careers in hydrogen power span research and development, engineering, manufacturing, and operations. Advanced fuel cell development, infrastructure deployment such as refueling stations, and hydrogen storage solutions are areas poised for substantial workforce expansion.
For example, the International Renewable Energy Agency forecasts that the global hydrogen economy could sustain millions of jobs by 2050. Pilot projects like Alberta’s hydrogen-fueled transportation initiatives in Canada are already creating opportunities across the supply chain, from infrastructure specialists to logisticians. Hydrogen’s ability to decarbonize challenging industries such as aviation, shipping, and heavy manufacturing could lead to high demand for workers with skills in these traditionally high-emission sectors.
Key Roles in Renewable Energy
The renewable energy revolution offers a wide variety of roles that cater to a diverse skill set, from hands-on labor to high-level engineering and management. Here are some of the energy job roles with their key positions that are shaping the energy workforce:
Solar Industry Roles
- Solar Installers: These workers handle the physical installation of solar panels on rooftops and in solar farms, requiring both technical skill and construction expertise.
- Manufacturing Technicians: These roles involve producing solar cells, modules, and supporting infrastructure. With domestic manufacturing rising in the US due to policy incentives, this sector offers significant growth potential.
- Project Developers: These professionals oversee project design, permitting, and execution for solar projects of all scales.
- Operations and Maintenance Specialists: As solar installations expand, maintaining their efficiency has become critical, fueling job growth in this area.
Hydrogen Energy Roles
- Fuel Cell Engineers: Key players in designing hydrogen-fueled technologies, providing solutions for vehicles, power generation, and industrial processes.
- Infrastructure Specialists: These roles focus on building and maintaining hydrogen pipelines, refueling stations, and storage solutions.
- Researchers and Chemists: Scientists in these roles continually innovate hydrogen production methods, including electrolysis and carbon capture.
Cross-Industry Opportunities
Renewable energy also creates numerous cross-industry roles in finance, marketing, IT, and education. Emerging technologies demand skilled data analysts, sustainability consultants, and workforce trainers to guide the green transition.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Investing in renewable energy jobs offers dual advantages—economic and environmental. Solar energy has already proven its ability to reduce household and business energy costs, freeing resources for other expenditures. Meanwhile, hydrogen offers low-carbon solutions for sectors that cannot easily shift to direct electrification, such as agriculture and heavy industry. Both sectors are pivotal to global decarbonization, helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Additionally, these industries contribute to local economies by creating high-quality jobs, enhancing energy security, and reducing reliance on imported fuels. By choosing career paths in solar energy and hydrogen power, workers not only gain financial security but also contribute to a sustainable future.
Shaping the Workforce of Tomorrow
The move toward renewables isn’t just good for the planet—it’s an unparalleled opportunity for economic growth and job creation. Whether through the continued expansion of solar energy or the evolving possibilities in hydrogen power, the renewable energy industry is cementing its role as the bedrock of the 21st-century workforce. By investing in training and education to equip workers with the necessary skills, we can ensure a smooth transition to a cleaner, brighter energy future.
What's Your Reaction?