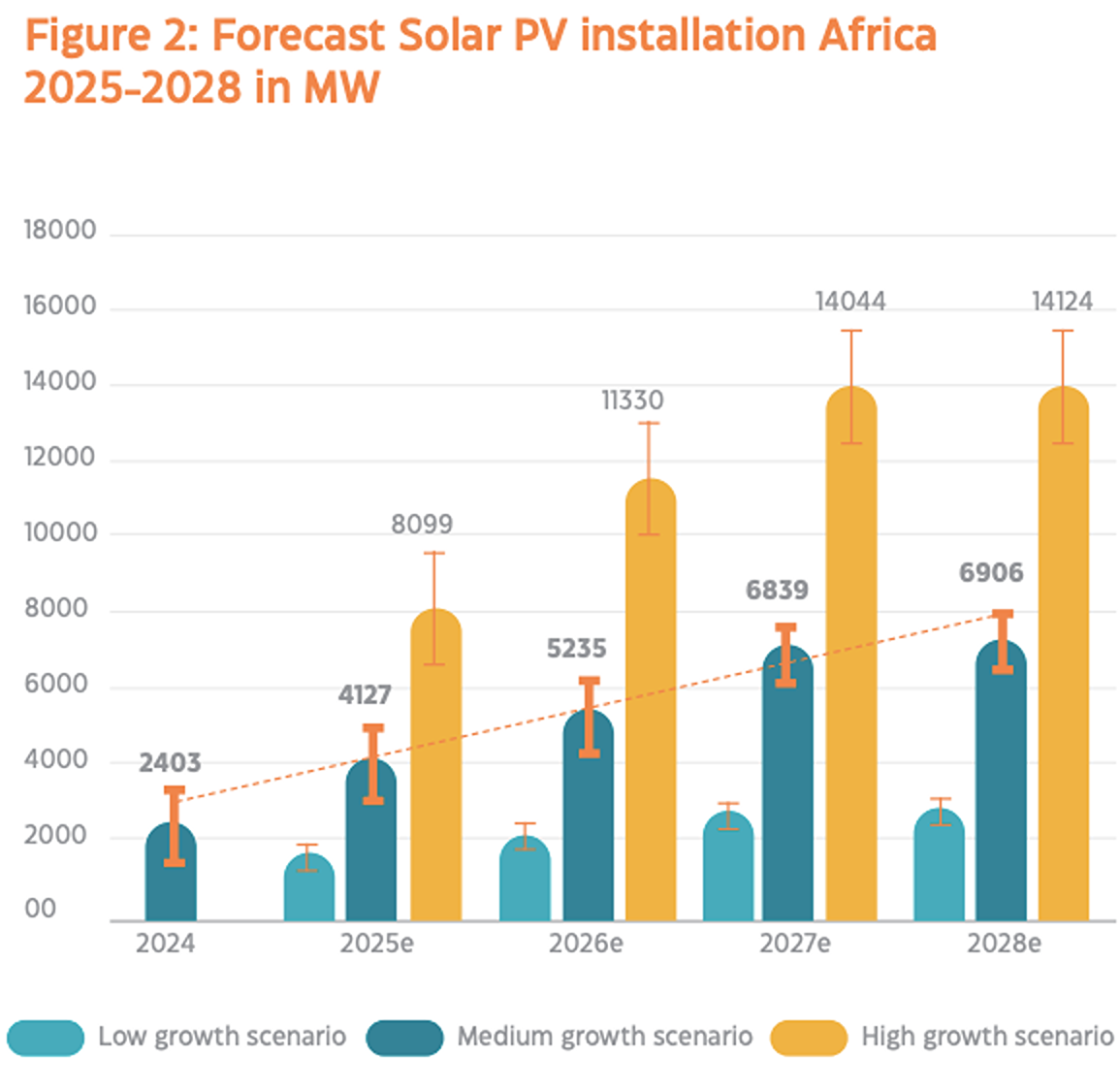
Hydrogen Engine Alliance of North America Pushing Forward Clean Energy Solutions
The Hydrogen Engine Alliance of North America (H2EA-NA) is making waves in the energy and transportation sectors with its mission…

The Hydrogen Engine Alliance of North America (H2EA-NA) is making waves in the energy and transportation sectors with its mission to advance hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines (H2-ICEs). By bringing together academics, industry leaders, and policymakers, the alliance is working to integrate this innovative technology into diverse applications, from vehicles to heavy equipment. Here’s a closer look at how this initiative could play a crucial role in the clean energy transition.
How Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engines Work
At its core, a hydrogen-powered internal combustion engine operates similarly to traditional gasoline or diesel engines—but with a critical difference. Instead of burning fossil fuels, H2-ICEs use hydrogen. Combustion occurs when hydrogen mixes with air inside the engine’s cylinders, producing energy to power the system. What’s particularly noteworthy is the output. Unlike diesel or gasoline engines that release carbon dioxide and harmful pollutants, the primary by-product of hydrogen combustion is water vapor, making it an environmentally friendly alternative.
The appeal of H2-ICEs goes beyond emissions. They leverage well-established engine technologies, which means industries don’t have to completely discard existing systems and expertise. This adaptability makes them a practical solution for heavy-duty vehicles, off-road equipment, and marine applications where the use of fully electric systems or hydrogen fuel cells might be less feasible due to performance limitations.
Recent Developments in Hydrogen Engine Technology
The H2EA-NA has been instrumental in fostering innovation to overcome the challenges of hydrogen technology. For instance, a recent addition to the alliance, Ionbond, has introduced advancements that address some of hydrogen’s unique material requirements. One of their standout contributions is specialized coatings for engine components. These coatings, such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) layers, help manage hydrogen’s low lubrication properties and reduce the risks of hydrogen embrittlement—a type of material weakness caused by hydrogen atoms permeating metal components.
Ionbond’s coatings also enhance the performance and durability of hydrogen injection systems, a critical aspect of the engine’s operation. By ensuring smoother surfaces and better seals, they help contain hydrogen molecules more effectively and improve system efficiency. These innovations are vital as H2-ICEs must withstand high vibrations, extreme temperatures, and demanding applications, particularly in industries like trucking and construction.
Global Interest Growing but the U.S. Lags Behind
While North America focuses on innovation, countries like Germany and China have already made significant strides in hydrogen technology adoption. For example, Germany’s Allianz Wasserstoffmotor is heavily invested in H2-ICE development. This momentum creates a competitive landscape where the U.S. must play catch-up.
The H2EA-NA is addressing these gaps by uniting academic institutions like the University of California, Riverside (UCR) and the University of Michigan, along with private-sector players. They aim to develop a network of hydrogen infrastructure while educating policymakers and the public on its benefits. However, barriers such as high costs, limited hydrogen refueling stations, and intricate regulatory hurdles remain substantial.
Environmental and Economic Potential
One of the most pressing concerns in transportation today is reducing emissions, particularly of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon dioxide. A noteworthy demonstration by Southwest Research Institute recently highlighted that hydrogen-powered trucks can achieve ultra-low NOx emissions, far outperforming their diesel counterparts. Results like these are pushing the industry and governments to see hydrogen as more than a theoretical solution—it’s becoming a practical alternative for decarbonizing sectors that find electrification challenging.
Beyond environmental benefits, the economic implications are significant. Hydrogen adoption could invigorate manufacturing industries, boost job creation in infrastructure development, and offer new opportunities for technological expertise in areas like coatings, refueling systems, and engine efficiency enhancements.
Challenges and Timelines for Adoption
Despite its potential, H2-ICE adoption faces considerable challenges. The technology itself, while promising, involves high developmental costs and complexity. For hydrogen to become a widespread fuel, robust supply chains and fueling stations need to be established. Currently, the availability of such infrastructure barely meets demand, causing delays in scaling.
Realistically, experts in the field predict that hydrogen engines will play a supplementary role alongside electric vehicles and fuel cells. For sectors like long-haul trucking and off-road equipment, hydrogen combustion engines could find a solid foothold within the next five to ten years, provided investments and policy support align quickly. The introduction of industry-driven conferences, such as the H2EA-NA’s inaugural event in 2025, will likely accelerate this timeline by sharing technical solutions and showcasing real-world applications.
Real-World Applications We Can Pursue Today
What can we do with hydrogen engines now? Well, promising pilot projects are already underway in heavy-duty trucking, construction equipment, and marine applications. Companies and researchers can use H2-ICEs to retrofit existing diesel systems for transitional purposes. Additionally, municipalities could invest in hydrogen-powered public transportation fleets to simultaneously lower emissions and test refueling infrastructure.
For consumers, hydrogen might feel more out of reach right now, but its use in industrial and transportation sectors plays a critical indirect role in reducing emissions across supply chains. Creating awareness and demand for low-carbon products can also drive the hydrogen wave forward.
Moving Toward a Hydrogen Future
The Hydrogen Engine Alliance of North America is not just building engines—it’s building the foundation for cleaner, more adaptable energy systems. Hydrogen combustion technology allows us to leverage familiar engine designs while making meaningful strides toward sustainability. While its commercial-scale adoption may still be a few years away, its targeted use today in heavy-duty and industrial sectors provides exciting possibilities.
This reminds us that the energy transition isn’t just about one big leap. It’s about taking steps—piloting projects, educating people, building infrastructure, and smoothing the path for future breakthroughs. Hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines represent one of these essential steps, offering a practical, scalable solution to a global problem we can’t afford to ignore.
What's Your Reaction?