Pathway to commercialization of aqueous sulfur-based redox flow batteries
Researchers in China have identified a series of engineering strategies to bring aqueous sulfur-based redox flow batteries closer to commercial production. Improving catalyst design, ion-selective membranes, and device integration will be key to solve this battery storage technology's issues.
Researchers in China have identified a series of engineering strategies to bring aqueous sulfur-based redox flow batteries closer to commercial production. Improving catalyst design, ion-selective membranes, and device integration will be key to solve this battery storage technology's issues.
From ESS News
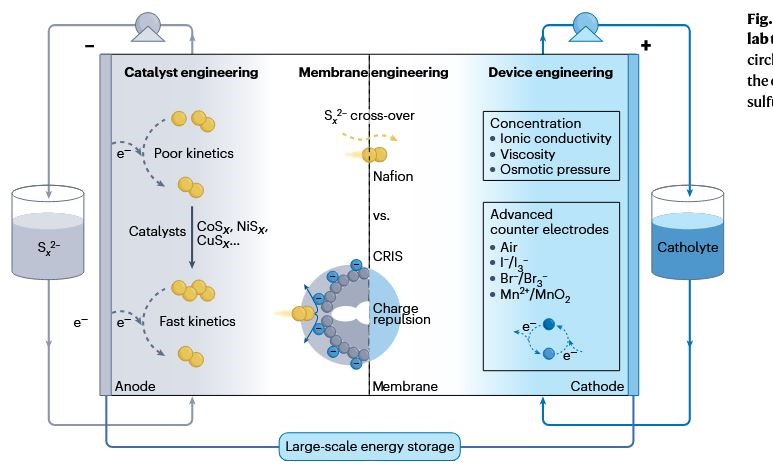
Polysulfide is one of the most promising materials for electrolytes used in large-scale aqueous redox flow batteries (RFBs) due to its inherent safety, high energy and low cost. However, potential polysulfide crossover results in a poor battery lifecycle, which prevents sulfur-based flow batteries from getting closer to commercialization.
With this in mind, a group of researchers in China has outlined a new pathway for the industrialization of this energy storage technology, which promises a competitive levelized cost of storage for long-duration energy storage. “In our work, we proposed an integrated strategy targeting sulfur-based flow battery commercialization, focusing on catalyst design, ion-selective membranes, and device integration,” the research's corresponding author, Dongliang Chao, told pv magazine.
To continue reading, please visit our ESS News website.
What's Your Reaction?























![[Upcoming Webinar] Addressing the Wind Industry's €25 Billion Annual Wake Loss Problem](https://www.windesco.com/hubfs/Swarm%20webinar%20cover%20image.png)