Understanding Current, Loads & Power Generation
When it comes to designing and installing solar electric systems, having a good grasp of the fundamentals is crucial. In this post, we'll briefly look into the types of electrical current, the various loads we need to power, and how photovoltaic (PV) modules generate electricity. This knowledge forms the foundation for determining the best PV ...

When it comes to designing and installing solar electric systems, having a good grasp of the fundamentals is crucial. In this post, we’ll briefly look into the types of electrical current, the various loads we need to power, and how photovoltaic (PV) modules generate electricity. This knowledge forms the foundation for determining the best PV system configuration for any given application.
 Types of Electrical Current: DC vs. AC
Types of Electrical Current: DC vs. AC
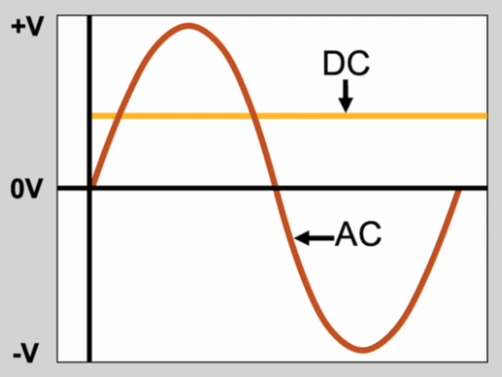
To start, let’s distinguish between the two main types of electrical current:
- Direct Current (DC)
- Characterized by a one-way movement of charge or electrons
- Represented graphically as a continuous straight line (orange line in image)
- Maintains a constant polarity relative to a reference point (usually positive)
- Generated by PV cells/modules and stored in/discharged by batteries
- Alternating Current (AC)
- Features a two-way movement of charge that alternates back and forth
- Represented graphically as a sine wave (brown line in image)
- Polarity changes periodically, creating cycles of positive and negative voltage
- Measured in Hertz (Hz), indicating the frequency of these cycles (commonly 50Hz or 60Hz)
- Provided by the utility grid, fossil fuel generators, and wind/hydro turbines
Understanding these current types is essential because different power sources and electrical devices operate on either AC or DC, which impacts system design and component selection. Devices can range from simple light bulbs to complex machinery. Regardless of their intricacies, it’s crucial to consider the types of loads a PV system will power when designing it:
- AC-only loads: most common in residential and commercial settings
- DC-only loads: often found in specialized applications or off-grid systems
- Dual-compatibility loads: less common, but can operate on both AC and DC
An interesting point to note is that many devices we typically plug into AC outlets actually run on DC internally. These devices use a converter or power supply (like the “brick” chargers for laptops or phones) to transform AC from the wall outlet into the DC that the device needs.
Photovoltaic Modules: The Heart of Solar Power
Let’s momentarily focus on the star of our solar electric systems: photovoltaic modules. These remarkable devices directly convert sunlight into DC electricity through the photovoltaic effect. While we won’t be going into this process in this post, here are some key points to understand about PV modules:
- They generate DC electricity when exposed to sunlight
- PV modules don’t need to be connected to a circuit to generate power; they create a potential difference when illuminated
- It’s safe to leave them exposed to sunlight even when not in use or when the system is shut off
 The PV Production Curve: A Day in the Life of a Solar Panel
The PV Production Curve: A Day in the Life of a Solar Panel
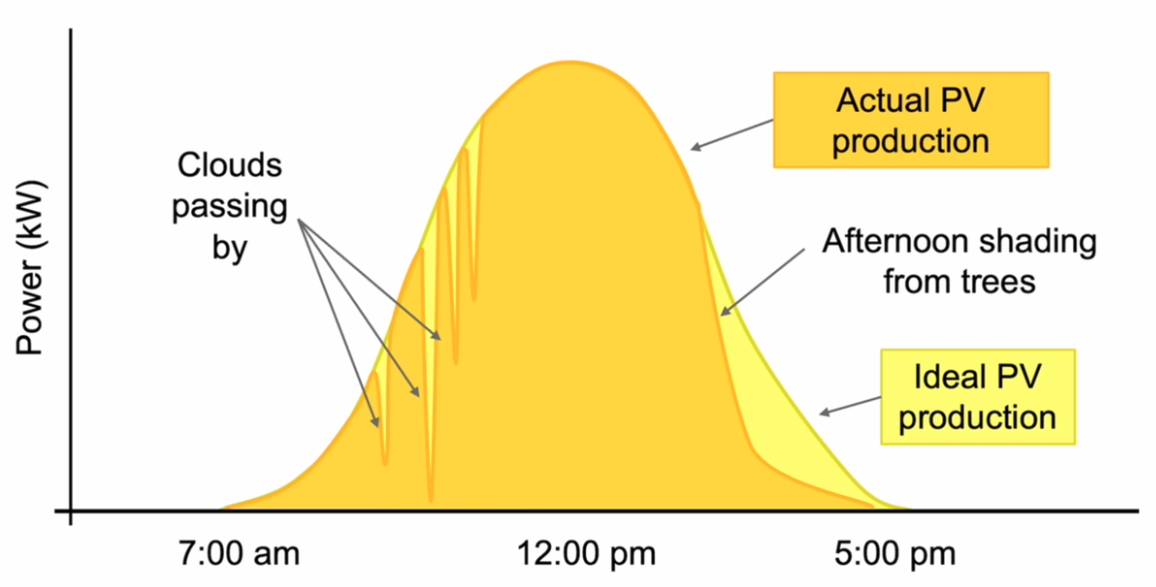
PV modules have a characteristic production curve that follows the sun’s path across the sky, including an “Ideal Scenario” coupled with “Real-World Factors”. In perfect conditions, a solar production curve resembles a bell shape that sees low production in the early morning as the sun rises, peak production around noon when the sun is highest, and a gradual decrease in the afternoon as the sun sets.
But Real-World Factors can affect this idealized curve, including passing clouds that cause sudden drops in production, morning fog or mist reducing early-day efficiency, afternoon shading from trees or structures when the sun is lower in the sky, and seasonal variations in sun angle and daylight hours.
Understanding this production curve is vital when designing PV systems as we need to consider how the PV system’s daily power generation aligns with the energy consumption patterns of the loads it will supply.
Matching PV Production to Load Demands
Understanding the PV production curve is vital when designing solar systems because one of the key challenges is aligning the solar production curve with the energy needs of device loads. This consideration often drives decisions about system components, configurations and beyond. In our most popular course, PVOL101, we begin to tie all of this together to equip you with the knowledge needed to properly design and install grid-directed PV systems. Topics include:
- PV Components and System Configurations
- Basics of Electricity
- Demand, PV Production and Incentives
- PV Modules and PV Module Performance
- Meter Testing, Series and Parallel
- Site Analysis
- PV Mounting Systems
- Grounding
- Inverters
- System Sizing
- Conductors and Wiring
- Best Safety Practices and Commissioning
- And much more!
By understanding these foundational concepts, you’ll be better equipped to design safe, efficient, and effective solar electric systems that meet specific energy needs while maximizing the incredible potential of solar power.
What's Your Reaction?