Novel MPPT technique for EV charging combined with PV, fuel cells
Scientists in India have designed a system that uses PV panels, a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell, battery storage, and a supercapacitor. It also relies on an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-based MPPT that reportedly achieves an efficiency of 98.7%.
Scientists in India have designed a system that uses PV panels, a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell, battery storage, and a supercapacitor. It also relies on an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-based MPPT that reportedly achieves an efficiency of 98.7%.
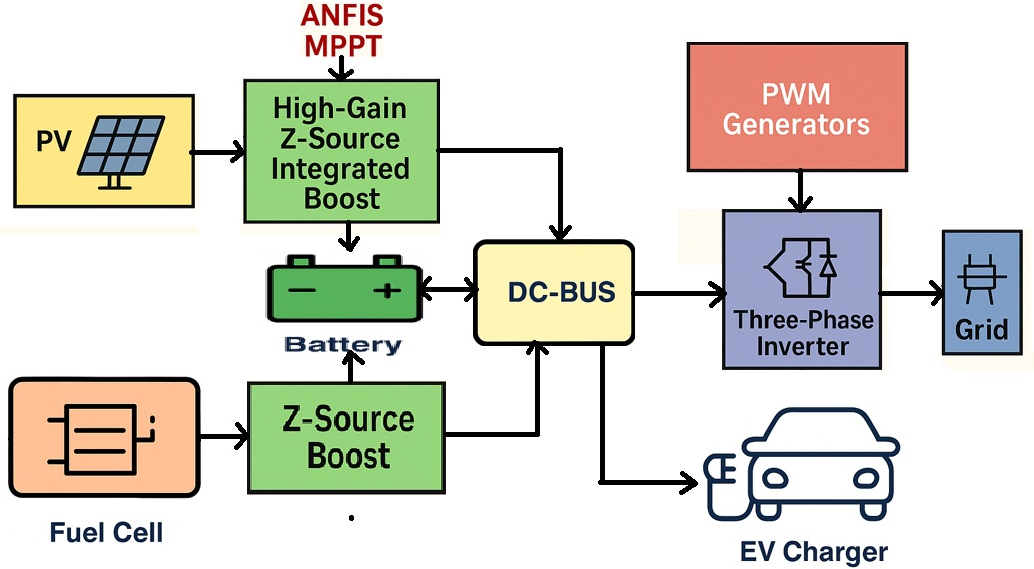
A research team led by scientists from India has developed a novel “smart” electric vehicle (EV) system that uses PV panels, a proton-exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell, battery storage, and a supercapacitor. At the core of the system lies a Z-source integrated boost converter with an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS)-based maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm.
“Unlike conventional PV-only or hybrid systems, this approach combines intelligent control with multi-source energy management to ensure efficient, stable, and reliable power delivery for smart EV charging applications,” corresponding author Suresh Vendoti told pv magazine. “In our future work, we will expand the concept to renewable-energy-based DC microgrids with vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capability, enabling smarter integration of EVs into the energy ecosystem.”
The system was simulated using MATLAB/Simulink 2021a. It included two 50 kW fast-charging units, a PV system with peak power of 186 kW, a lead-acid battery (BAT), and a hydrogen-based energy storage system (ESS). The hydrogen ESS includes a 176 kVA hydrogen production system, six 66 kW fuel cell (FC) modules, and a 450 kg hydrogen tank.
The system
The system is integrated using Z-source converters (ZSCs), where an impedance network connects the PV system, BAT, and the grid. The design of the ZSC includes two synchronously controlled switches, an input diode, an output diode, and a capacitor, and operates either in continuous conduction mode (CCM) or discontinuous conduction mode (DCM).
“An ANFIS-based MPPT method is proposed to optimize solar panel output under varying weather conditions. It uses PV voltage, current, and temperature as input variables, with the duty cycle as the output to control a DC-DC switched boost Landsman converter for maximum power tracking,” explained the academics. “With sufficient training epochs, ANFIS optimizes MPPT performance by refining fuzzy rules and minimizing errors, making it ready for real-time control applications.”
That system was verified with a lab-scale prototype, using FC with an output voltage of 100 V and an output current of 30-40 A; a DC-DC convertor with an output voltage of 1,000-1,100 V and an output current of 30 A; and a battery with 120 V of voltage. The error between the simulation and the prototype ranged between 0.8% and 3%, depending on the parameter.
Performance
“Simulation results demonstrate effective voltage boosting from 110 V to 150 V and a regulated output of approximately 1100 V at 30 A, with the PV-side current stabilized at 500 A. The fuel cell maintains a steady output of 110 V while its current decreases from 40 A to 25 A, and the battery retains a 60% state-of-charge (SOC) at 120 V output,” the results showed. “The hardware prototype, developed using a DSPIC30F4011 microcontroller, achieves an MPPT efficiency of 98.7%, voltage regulation within ± 1.5%, and output power deviation under 2%. Grid voltage and current waveforms exhibit low total harmonic distortion (THD), in compliance with IEEE 519 standards, with measured values of 500 V and 13 A, respectively.”
Concluding, Vendoti said that “the most striking result was the significant improvement in tracking efficiency and dynamic performance of the ANFIS-based MPPT under fluctuating solar irradiance compared to conventional MPPT algorithms. Additionally, the hybrid configuration proved capable of maintaining grid stability and uninterrupted EV charging, even under variable renewable generation and load demand, which exceeded initial expectations.”
The details of the system can be found in “Grid tied hybrid PV fuel cell system with energy storage and ANFIS based MPPT for smart EV charging,” published in Scientific Reports. Researchers from India’s Godavari Global University, St. Ann’s College of Engineering and Technology, GMR Institute of Technology, New Horizon College of Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Thailand’s Shinawatra University, Saudi Arabia’s Taif University, and Ethiopia’s Wollo University have participated in the study.
What's Your Reaction?